class: right, middle, my-title, title-slide # Fragile ecosystems, robust assessments? ## (What I did with my summer vacation) ### Sarah Gaichas, Isaac Kaplan, Patrick Lynch, and Christine Stawitz <br /> Northeast and Northwest Fisheries Science Centers, <br /> and Office of Science & Technology <br /> <br /> <br />Supported by Institute of Marine Research Norway, and NOAA NMFS International Fellowship --- class: top, left background-image: url("EDAB_images/IMG_4195.jpg") background-size: cover ## Summer Vacation ??? Greece, Crete, near the cave of Polypheomos --- background-image: url("EDAB_images/IMG_5562.jpg") background-size: cover ## Summer Vacation ??? Greece, Crete, near the cave of Polypheomos --- background-image: url("EDAB_images/IMG_5472.jpg") background-size: cover ## Summer Vacation ??? Greece, Crete, near the cave of Polypheomos --- ## Summer Vacation .pull-left-40[  ] .pull-right-60[  ] ??? Greece, Crete, near the cave of Polypheomos --- ## Odysseus and the Cyclops Polyphemus .pull-left[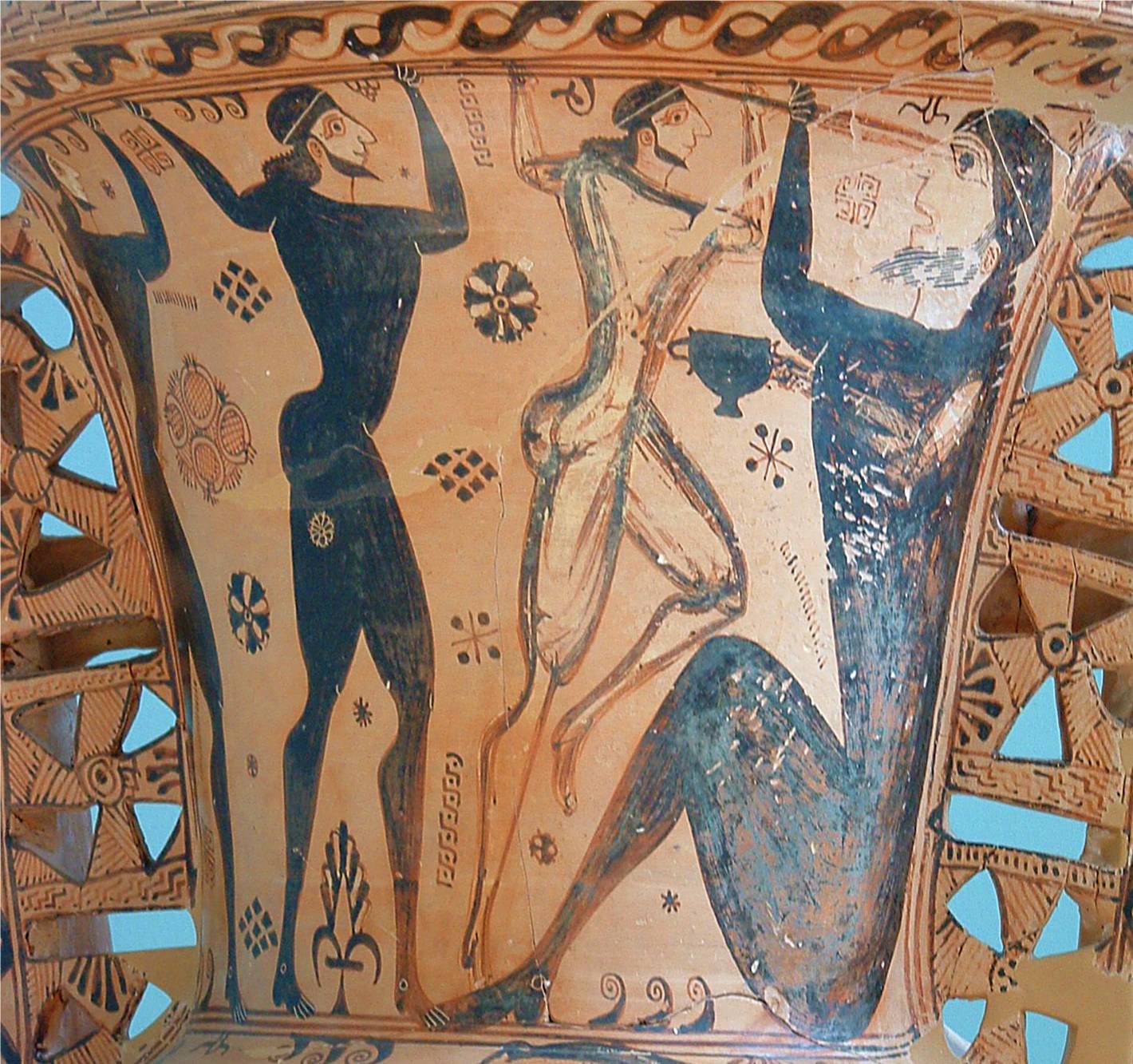  ] .pull-right[  ] By <a href="https://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Napoleon_Vier" class="extiw" title="nl:User:Napoleon Vier">Napoleon Vier</a>, <a href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/" title="Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0">CC BY-SA 3.0</a>, <a href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1353019">Link</a> .footnote[ https://www.ancientworldmagazine.com/articles/blinding-polyphemus/ ] --- <a href="https://www.storyboardthat.com/storyboards/jolinlabberton/odyssey-storyboard"><img src="//sbt.blob.core.windows.net/storyboards/jolinlabberton/odyssey-storyboard.png" /></a> <br> <a href="https://www.storyboardthat.com">Made with Storyboard That</a> --- <img src="EDAB_images/Cell-Col-0-Row-0.png" width="73%" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- <img src="EDAB_images/Cell-Col-1-Row-0.png" width="73%" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- <img src="EDAB_images/Cell-Col-2-Row-0.png" width="73%" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- <img src="EDAB_images/Cell-Col-0-Row-1.png" width="73%" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- <img src="EDAB_images/Cell-Col-1-Row-1.png" width="73%" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- <img src="EDAB_images/Cell-Col-2-Row-1.png" width="73%" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> ??? Hubris will sink you (or substantially delay achieving your objectives, and at great cost) Things change; workarounds are important testing is a theme (hypotheses, skills, each other) --- # Things we learn about Poseidon * Tricky: unforseen challenges * Vengeful: high cost of overconfidence  --- # Things we learn from Odysseus * Test your models * Guard your Personally Identifiable Information (PII)  --- ## We use models for a lot   --- ## What kinds of models are there?  --- ## How do we know they are right? * Fits to historical data (hindcast) * Influence of data over time (retrospective diagnostics) * Keep as simple and focused as possible * Simulation testing ## But What if ## data are noisy? ## we need to model complex interactions? ## conditions change over time? --- ## Fragile ecosystems, robust assessments? Performance testing stock assessments for the California Current and Nordic and Barents Seas under climate change .pull-left[ - Scientist exchange central to this project - NOAA internal "international fellowship" and REDUS funding: - Gaichas, April 15 - June 15 - Lynch, April 18 - June 7 - Kaplan, May 11 - June 21 - Christine Stawitz, May 19-25 ] .pull-right[  *<sup>1</sup>* ] - Additional NMFS and IMR collaborators with diverse skills and experiences - Kelli Johnson, Gavin Fay, Emma Hodgson, other stock assessment and modeling folks - Cecilie Hansen, Daniel Howell, Erik Olsen, and now **YOU** .footnote[ [1] https://www.meganstarr.com/30-things-you-should-know-before-moving-to-norway/ ] --- # Project motivation .pull-left[ - Changing climate and ocean conditions → Shifting distributions, changing productivity - Needs: - Improve our ability to project global change impacts in the California Current and Nordic/Barents Seas (and elsewhere) - Test the performance of stock assessments to these impacts ] .pull-right[ *Climate-Ready Management<sup>1</sup>*  ] .footnote[ [1] Karp, Melissa A. et al. 2019. Accounting for shifting distributionsand changing productivity in the development of scientific advice for fishery management. – ICES Journal of Marine Science, doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsz048. ] ??? --- ## End-to-end ecosystem operating models Atlantis modeling framework: [Fulton et al. 2011](https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1467-2979.2011.00412.x), [Fulton and Smith 2004](https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajms/article/view/33182) .pull-left[ **Norwegian-Barents Sea** [Hansen et al. 2016](https://www.imr.no/filarkiv/2016/04/fh-2-2016_noba_atlantis_model_til_web.pdf/nn-no), [2018](https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0210419)  ] .pull-right[ **California Current** [Marshall et al. 2017](https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/gcb.13594), [Kaplan et al. 2017](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304380016308262?via%3Dihub)  ] Building on global change projections: [Hodgson et al. 2018](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304380018301856?via%3Dihub), [Olsen et al. 2018](https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2018.00064/full) ??? --- ## Project overview .pull-left[ 1. Scenarios for effects of temperature on growth, natural mortality 1. Focus on key stocks (Northeast Arctic cod, Norwegian spring spawning herring, California Current sardine, Pacific hake or a Pacific rockfish) 1. Atlantis output → dataset generator (`atlantisom`) → Stock Synthesis assessment 1. Compare performance of different model settings, multiple models, model ensembles ] .pull-right[ <img src="EDAB_images/CCAclimatescenario.png" width="921" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> ] Bonus: `atlantisom` → multispecies, other single species models for testing ??? --- ## Test both estimation and (simple) MSE capability <img src="EDAB_images/PoseidonDesign.png" width="1709" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- ## Design: Operating model scenario (climate and fishing) <img src="EDAB_images/projectionOMsetup.png" width="85%" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> -- .pull-left[ * Recruitment variability in the operating model * Specify uncertainty in assessment inputs using `atlantisom` ] .pull-right[  ] --- ## Climate impacts in the operating model  .footnote[ Hodgson, E. E., Kaplan, I. C., Marshall, K. N., Leonard, J., Essington, T. E., Busch, D. S., Fulton, E. A., et al. 2018. Consequences of spatially variable ocean acidification in the California Current: Lower pH drives strongest declines in benthic species in southern regions while greatest economic impacts occur in northern regions. Ecological Modelling, 383: 106–117. Marshall, K. N., Kaplan, I. C., Hodgson, E. E., Hermann, A., Busch, D. S., McElhany, P., Essington, T. E., et al. 2017. Risks of ocean acidification in the California Current food web and fisheries: ecosystem model projections. Global Change Biology, 23: 1525–1539. ] --- ## Climate impacts in the operating model  .footnote[ Hodgson, E. E., Kaplan, I. C., Marshall, K. N., Leonard, J., Essington, T. E., Busch, D. S., Fulton, E. A., et al. 2018. Consequences of spatially variable ocean acidification in the California Current: Lower pH drives strongest declines in benthic species in southern regions while greatest economic impacts occur in northern regions. Ecological Modelling, 383: 106–117. Marshall, K. N., Kaplan, I. C., Hodgson, E. E., Hermann, A., Busch, D. S., McElhany, P., Essington, T. E., et al. 2017. Risks of ocean acidification in the California Current food web and fisheries: ecosystem model projections. Global Change Biology, 23: 1525–1539. ] --- ## Climate + cumulative impacts in the operating model  --- ## Stock assessment uncertainty * Focus on climate impacts to growth and natural mortality (productivity) * Full factorial design over common stock assessment assumptions * Growth: 1. constant growth parameters 1. regime shifts in growth parameters ([Stawitz et al. 2019](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0165783619300049?via%3Dihub)) 1. empirical weight-at-age ([Kuriyama et al. 2016](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0165783615300837)) * Natural mortality: 1. fixed at an “uninformed” constant value of 0.2 1. fixed at a constant value that reflects the true average value (over time) from the OM 1. establishing regimes by fixing at the true average values from the OM over specified time blocks * Also, an equally weighted ensemble of the 9 estimation models * Stock synthesis framework initially, but extend to other assessment models, generalize, and learn from Norwegian data and assessment framework --- ## Experimental design <img src="EDAB_images/expdesignfig.png" width="80%" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- ## Make atlantis output into assessment model input Example workflows: 1. Get true biomass, abundance, age composition, length composition, weight at age, fishery catch, fishery catch at age, fishery length composition, and fishery weight age age for a "sardine-like species": https://sgaichas.github.io/poseidon-dev/FullSardineTruthEx.html 1. Format these outputs and get other life history parameters for input into a stock assessment model ([Stock Synthesis](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0165783612003293), using [`r4ss`](https://github.com/r4ss)): https://sgaichas.github.io/poseidon-dev/CreateStockSynthesis.html 1. Get true and observed input data, format inputs, and run the assessment model: https://sgaichas.github.io/poseidon-dev/SardinesHakeatlantisom2SStest.html 1. In progress: compare assessment results with truth: https://sgaichas.github.io/poseidon-dev/SkillAssessInit.html --- ## What can we do so far? .pull-left[ Survey census test NOBA <img src="EDAB_images/NOBAcensus.png" width="1792" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> True length composition NOBA <img src="EDAB_images/NOBAherringtruelf.png" width="1792" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> ] .pull-right[ Standard survey test CCA <img src="EDAB_images/CCsurveyex.png" width="1792" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> Survey length composition CCA <img src="EDAB_images/CCV3herringlfcomp.png" width="1792" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> ] --- ## A "sardine" assessment Need: assessment model data inputs and life history parameters *(model based on actual Sardine assessment in Stock Synthesis 3)* .pull-left[ Data: * survey biomass index * survey length composition * survey age composition (conditional catch at age) * fishery catch (tons) * fishery length composition * fishery age composition ] .pull-right[ Parameters: * natural mortality (from total mortality) * growth curve (from survey length at age) * maturity at age (true) * unfished recruitment and steepness (true) * weight-length curve (true) ] --- ## A "sardine" assessment: setup * California Current Atlantis run with and without climate signal * Input data generated (e.g. sardine survey, below in green) * Parameters derived; simpler recruitment distribution <img src="EDAB_images/CCsurvObsBiom.png" width="90%" style="display: block; margin: auto auto auto 0;" /> --- ## A "sardine" assessment: fits to data .pull-left[   ] .pull-right[   ] --- ## A "sardine" assessment: skill? (proof of concept) .pull-left[ Biomass <img src="EDAB_images/trueBss3B.png" width="1792" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> Fishing mortality <img src="EDAB_images/trueFss3F.png" width="1792" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> ] .pull-right[ Recruitment <img src="EDAB_images/trueRss3R.png" width="1792" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> Key: <span style="color:teal">True</span> <span style="color:red">SS3 estimate</span> ] --- ## Full disclosure! .pull-left-60[ Still working on: 1. Functions for older Atlantis codebases (i.e., CCA model) 1. Splitting aggregate age groups into true ages 1. Interpolating aggregate age groups weight at age for true ages 1. Fishery catch weight by area 1. Wrapper functions to generate data in fewer steps 1. Automated skill assessment functions 1. Inputs for models other than Stock Synthesis ] .pull-right-40[  ] --- ## Specify uncertainty in assessment "data": What Would Poseidon Do? What level of uncertainty is appropriate to carry through these analyses? .pull-left[ 1. Biological: 1. appropriate sigma-R? 1. Survey specification: 1. timing and spatial coverage? 1. which species are captured? 1. species-specific survey efficiency ("q")? 1. selectivity at age for each species? ] .pull-right[ 1. Survey uncertainty: 1. additional observation error (survey cv for index)? 1. effective sample size for biological samples? 1. Fishery uncertainty: 1. additional observation error (catch cv for total)? 1. catch sampled for length/age in all areas? 1. effective sample size for biological samples? ] --- ## P.S. What else could we test?  .footnote[ https://xkcd.com/1885/ ] --- ## External Resources * [Atlantis Model Documentation](https://github.com/Atlantis-Ecosystem-Model/Atlantis_example_and_instructions) * [atlantisom R package](https://github.com/r4atlantis/atlantisom) * [Testing atlantisom](https://github.com/sgaichas/poseidon-dev) * Slides available at https://noaa-edab.github.io/presentations --- background-image: url("EDAB_images/IMG_2733.jpg") background-size: cover ## Questions? # Tusen Takk til Havforskningsinstituttet! --- background-image: url("EDAB_images/IMG_5809.jpg") background-size: cover